30
How a Microwave Works
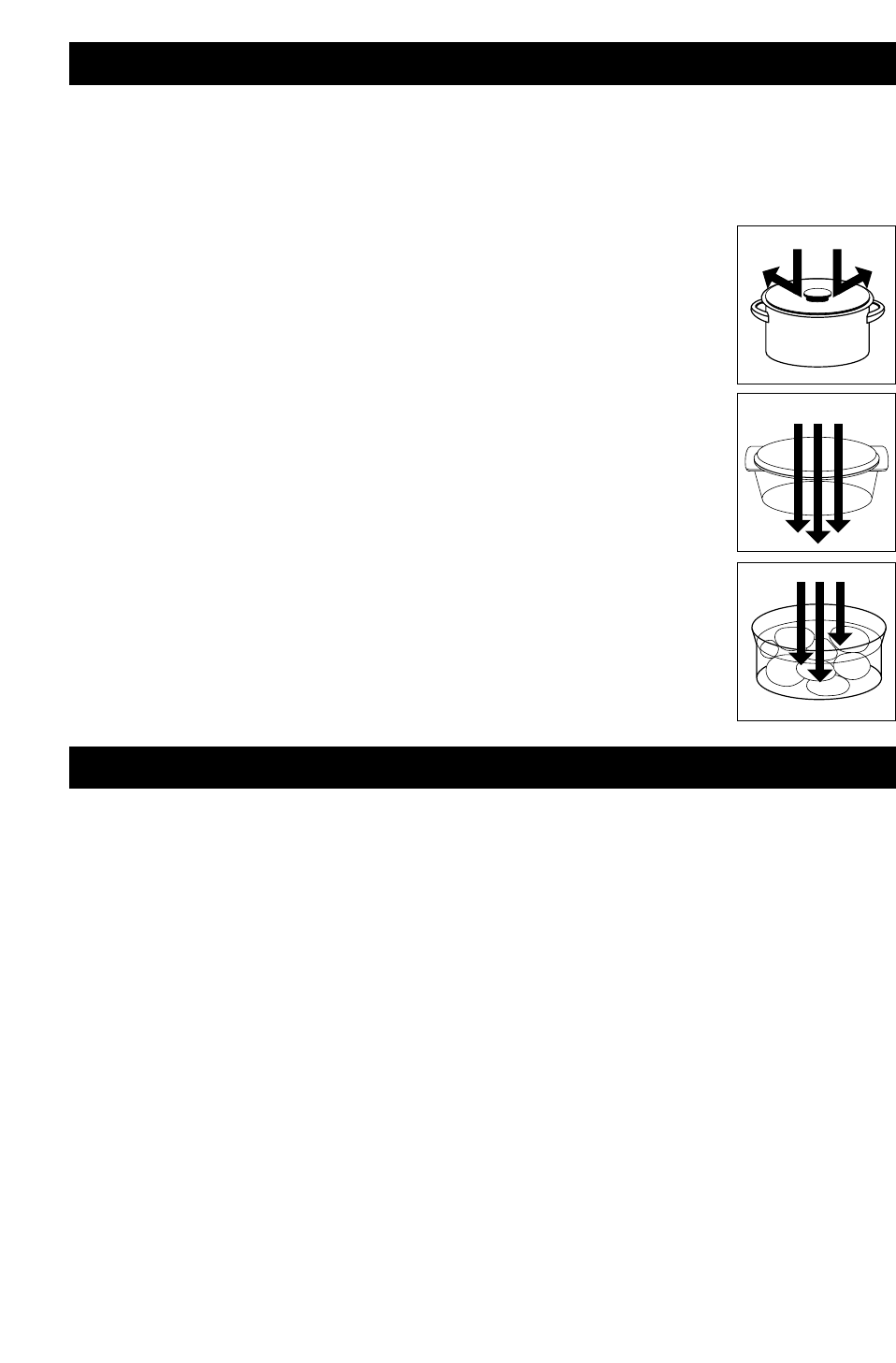
1.Reflection
They will REFLECT off metal. The inner walls of your oven are made of stainless
steel, so that the microwave energy can bounce evenly around the cavity.
Of course, the microwaves will also reflect off metal cooking containers and
accessories, such as saucepans and platters. For this reason, NEVER use the Wire
Rack Shelf on Microwave only.
2.Transmission
The microwaves will TRANSMIT through paper, plastic, glass and china and,
therefore, it is containers made of these substances that are used in microwave
cookery.
3.Absorption
The microwave energy is ABSORBED by the food. The energy penetrates the
outside area of the food causing the molecules to vibrate over 2,450,000,000 times
a second. This vibration causes the water molecules to rub against each other
producing frictional heat which cooks this outer part of the food; the heat is then
couducted through the food to cook the centre. Food, therefore, cooks from the
outside, inwards.
Standing Time
The heat that builds up on the outside of the food is still being conducted to the centre, even after the
microwave oven has switched off. This period is know as the “Standing Time”. The time it takes for the food to
finish cooking will vary depending on its shape, size and type. For example, a jacket potato will need to stand
for at least 5-10 minutes after the end of the cooking time and during this time the temperature at the centre will
increase. A pastry pie that has been reheated will only need a standing time of 1-2 minutes for heat to
distribute evenly.
If the food is put back in the Microwave and heated again before the standing time has elapsed, the food can
very quickly become overcooked.
To get the most from your Panasonic Combi it is helpful to understand how the oven works as a Microwave.
Once connected to an outlet, the electricity flows along the flex and is converted into microwave energy by the
MAGNETRON. Microwaves are ultra high frequency waves, and belong to the same category as radio and
television waves. These are directed into the cavity through the WAVE GUIDE.
When they reach the cavity, the microwaves will behave in one of three ways: