35
RQT6536
Reference Advanced Operations
34
RQT6536
Advanced Operations
Bitstream
This is the digital form of multi-channel audio
data (e.g., 5.1 channel) before it is decoded into
its various channels.
Decoder
A decoder restores the coded audio signals on
DVDs to normal. This is called decoding.
Dolby Digital
This is a method of coding digital signals devel-
oped by Dolby Laboratories. Apart from stereo
(2-channel) audio, these signals can also be
multi-channel audio. A large amount of audio
information can be recorded on the disc using
this method.
Dolby Pro Logic
A surround system where a 4-channel audio
track is recorded as 2 channels and then is re-
stored to 4 channels for play. The surround chan-
nel is monaural and can reproduce up to 7 kHz.
DTS (Digital Theater Systems)
This surround system is used in many movie the-
aters around the world. There is good separation
between the channels, so realistic sound effects
are possible.
Dynamic range
Dynamic range is the difference between the
lowest level of sound that can be heard above
the noise of the equipment and the highest level
of sound before distortion occurs.
Frame still and field still
A still is shown when you pause a moving
picture. A frame still is made up of 2 alternating
fields, so the picture may appear blurred, but
overall quality is high.
A field still is not blurred, but it has only half the
information of a frame still so picture quality is
lower.
I/P/B
MPEG 2, the video compression standard adopt-
ed for use with DVD-Video, codes frames using
these 3 picture types.
I: Intra coded picture
This picture has the best quality and is the
best to use when adjusting the picture.
P: Predictive coded picture
This picture is calculated based on past I or
P-pictures.
B: Bidirectionally-predictive coded picture
This picture is calculated by comparing past
and future I and P-pictures so it has the
lowest volume of information.
Linear PCM (pulse code modulation)
These are uncompressed digital signals, similar
to those found on CDs.
Playback control (PBC)
If a Video CD has playback control, you can
select scenes and information with menus.
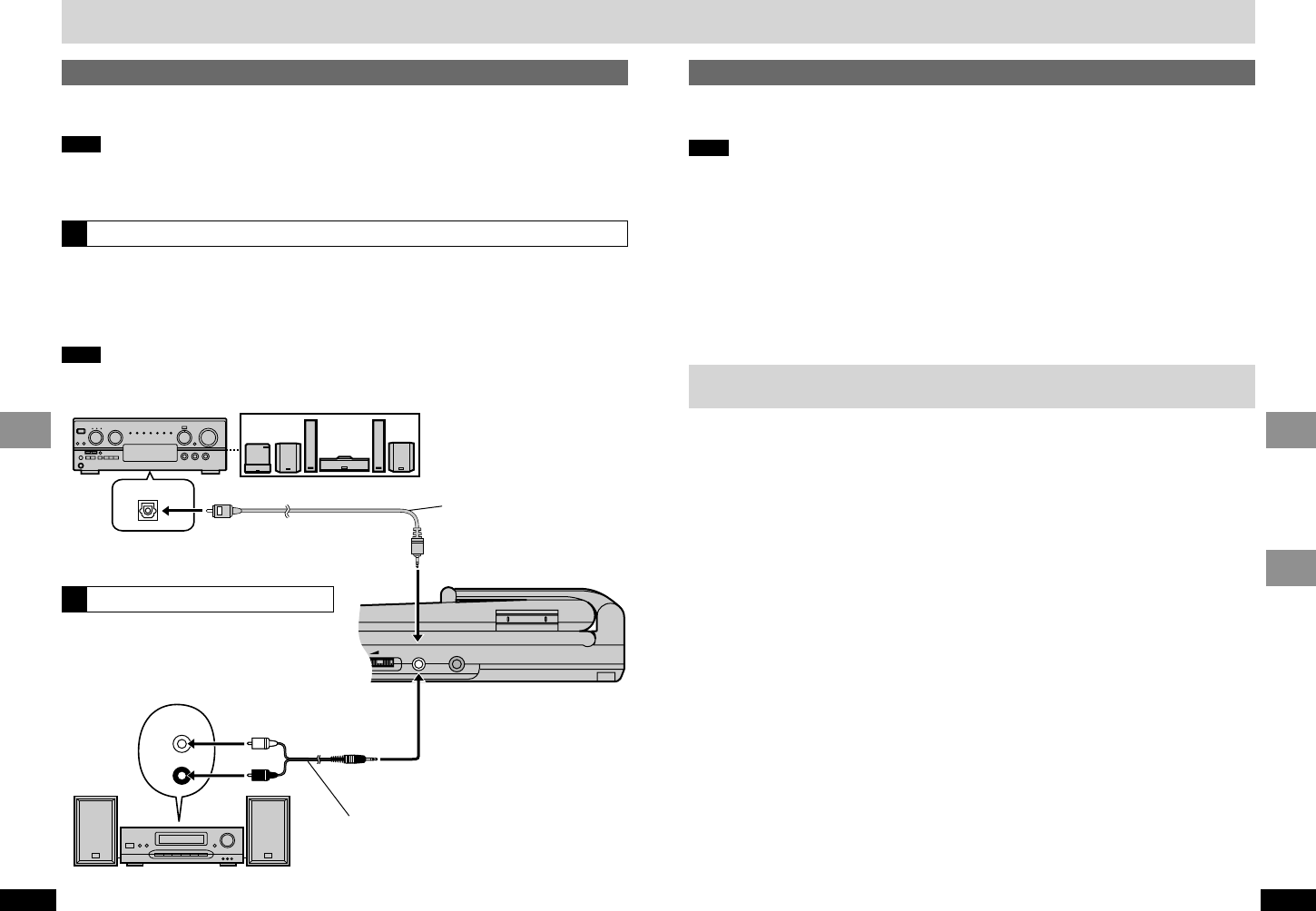
Recording to digital recording equipment or cassette tapes
≥Digital recording
You can record the digital signal directly to digital recording equipment.
Connect the recording equipment with an optical fiber cable (➡ [A] page 34).
Note
≥With DVD, the following conditions must be met: a the disc doesn’t have protection preventing
digital recording, and b the recording equipment can handle signals with a sampling frequency of
48 kHz.
≥You cannot record MP3.
When recording DVDs, make the following settings.
ADVANCED SURROUND: OFF (➡ page 24)
PCM Down Conversion: Yes (➡ page 29)
Dolby Digital/DTS Digital Surround: PCM (➡ page 29)
≥Analogue recording
You can record to a cassette deck or other recording equipment. Connect the recording equipment
with a stereo connection cable (➡ [B] page 34). There are no limitations on recording analogue signals
as there are with digital signals.
Glossary
Enjoying more powerful sound
This model can play Dolby Digital and DTS, but only in two channels. You must connect a unit with a
Dolby Digital or DTS decoder to enjoy surround sound.
Note
≥The equipment connections described are examples.
≥Peripheral equipment and optional cables sold separately unless otherwise indicated.
≥Before connection, turn off all equipment and read the appropriate operating instructions.
To enjoy stereo or Dolby Pro Logic
Connect a digital amplifier or system component.
≥Change the settings in “Digital output”
≥(➡ page 29).
Digital connection
To enjoy multi-channel surround sound
Connect an amplifier with a built-in decoder or a
decoder-amplifier combination.
≥Change the settings in “Digital output”
(➡ page 29).
Note
You cannot use DTS Digital Surround
decoders not suited to DVD.