29
b) Measuring AC and DC voltage
ƽ
Do not exceed the permitted max. input values; this also applies when measuring
superimposed direct voltages (e.g. ripple voltages).
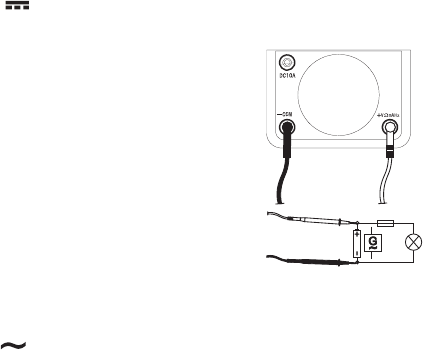
Proceed as follows to measure DC voltages:
- Select the measuring range DCV using the rotary switch.
- Connect the black measuring line with the COM socket (6) and
the red measuring line with the VΩ socket (7).
- Now perform null balancing.
- Observe the correct polarity (red = + / black = -) and connect the
two test prods with the test object (battery, circuit, etc.).
- If the polarity is not correct, no value is displayed. The built-in pro-
tective diode prevents the measurement. Stop measuring and
measure again observing the right polarity.
- Read off the measured value on the “V” scale.
- After measuring, put the rotary switch in the “OFF” position to turn
off the multimeter.
Proceed as follows to measure AC voltages:
- Select the measuring range ACV on the rotary switch.
- Connect the black measuring line with the COM socket (6) and the red measuring line with the VΩ
socket (7).
- Now perform null balancing.
- Connect the two test prods to the test object (battery, switch etc.).
- Read off the measured value on the “V” scale.
- After measuring, put the rotary switch in the “OFF” position to turn off the multimeter.
☞
In the AC measuring range, pressing the “Vrms/Vp-p” (8) button switches between the dis-
play of the rms value (Vrms) and the peak value (Vp-p). When the button is pressed in, the
peak value function is active.