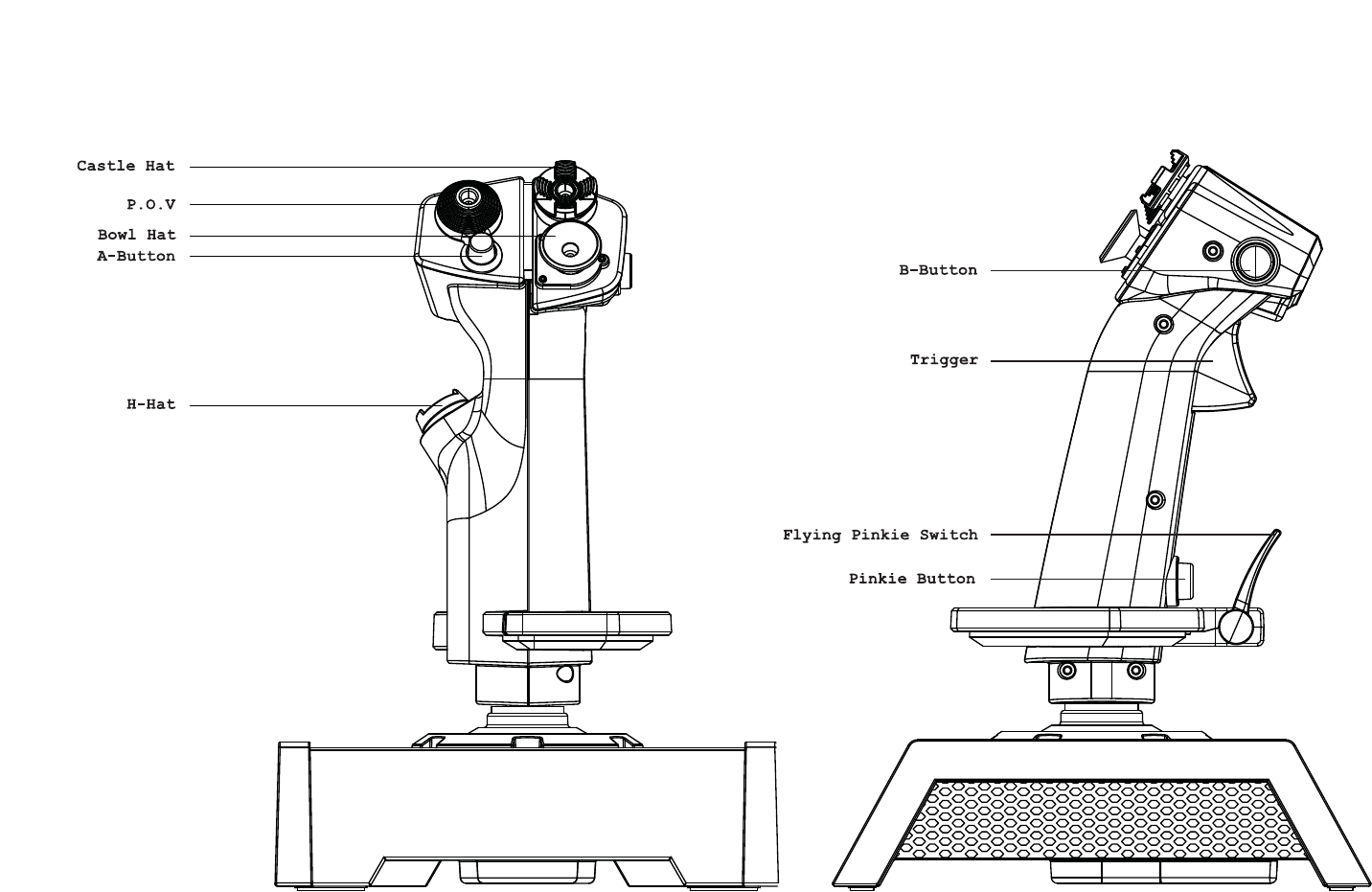
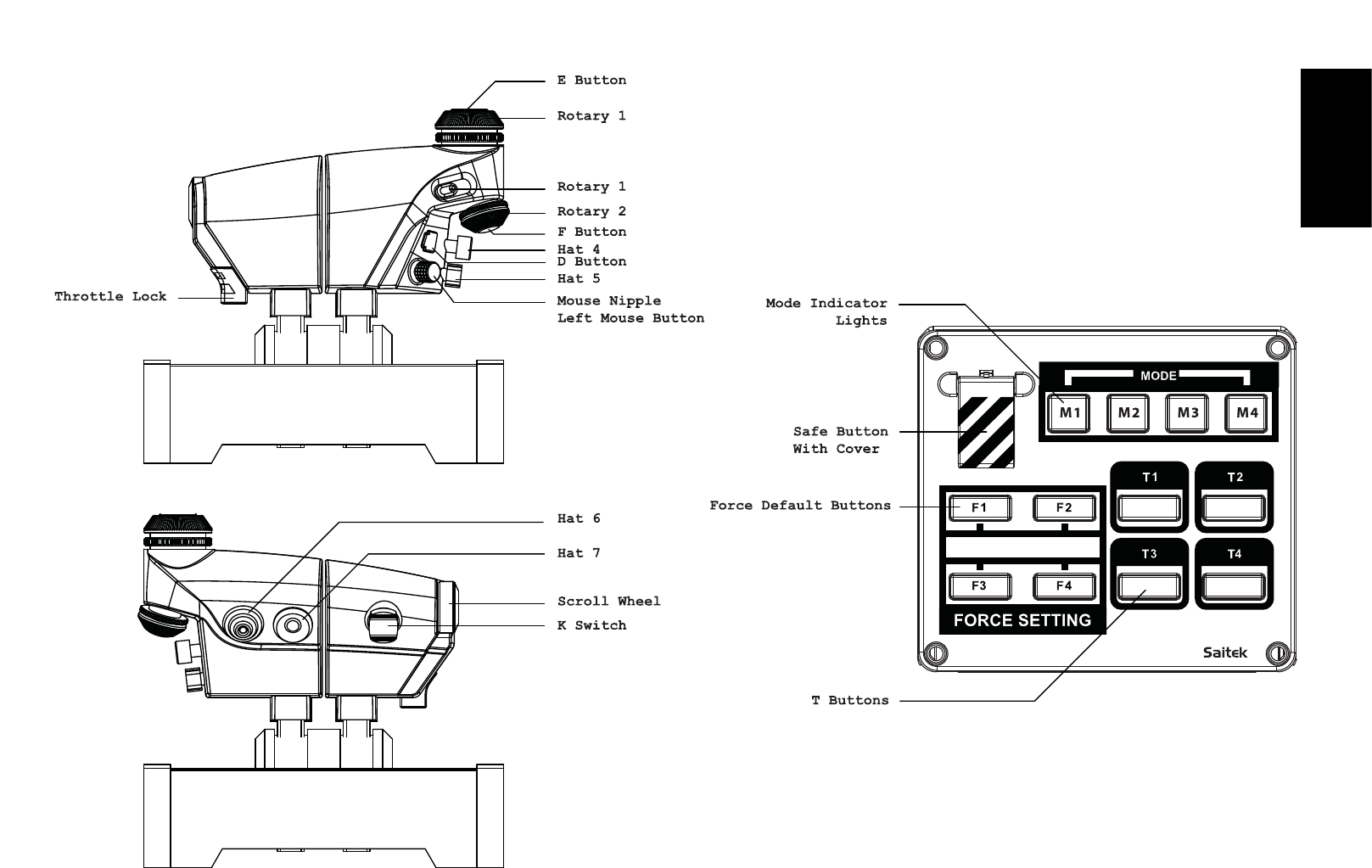
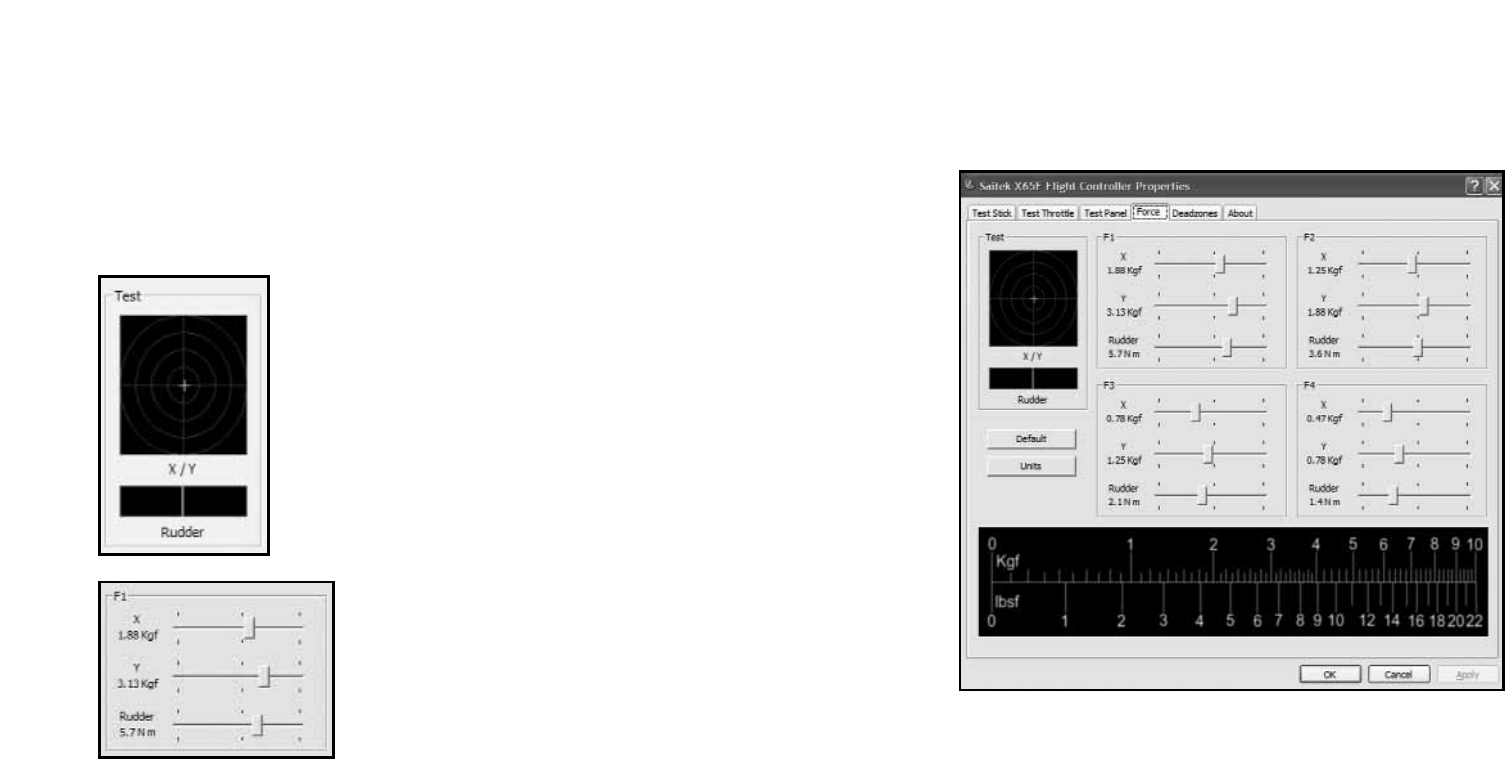
ENGLISHENGLISHDEUTSCHENGLISHENGLISH
44
5. Totzonen
Dieser Bildschirm ist in zwei Hauptbereiche unterteilt. Sie können hier sowohl die
Totzonen-Einstellungen für alle sieben Achsen und die beiden Mausachsen
vornehmen, als auch die Achsen-Kurve für X-, Y- und Ruder-Achse angleichen.
Diese beiden Features werden im Folgenden erklärt. Beginnen wir mit den
Totzonen.
Was ist eine Totzone?
Eine Totzone ist ein Bereich, innerhalb dessen die Bewegung einer Achse von den
Treibern nicht erkannt wird, und somit keine Auswirkung auf das laufende Spiel hat. Eine
Totzone kann um den Mittelpunkt eines Achsen-Radius liegen, oder an jedem beliebigen
Ende. Sie können Totzonen für alle sieben Achsen festlegen, X-, Y- und Ruder-Achse,
Schubhebel 1, Schubhebel 2, Rotary 1 und Rotary 2, sowie für den Maus-Nippel, der für
links, rechts, aufwärts und abwärts separate Bänder hat. Wenn Sie beispielsweise Ihren
Stick nur in der X-Achse bewegen
möchten, es aber schwierig finden,
dabei Bewegungen der Y-Achse zu
vermeiden, können Sie eine Totzone
für die Y-Achse definieren, damit
diese kleinen Bewegungen von den
Treibern nicht erkannt werden.
Einrichten der Totzonen
Jede Achse wird von einer weißen Box repräsentiert, die eine rote Linie enthält. Diese zeigt an, wo sich die jeweilige Achse gerade befindet. Das
Bewegen einer Achse bewegt die entsprechende rote Linie. Mit Hilfe dieser Linien können Sie exakt bestimmen, wo eine Totzone beginnen und enden
soll. Unter jeder Box befindet sich eine Gleitskala. Verwenden Sie diese, um die Größe der Totzonen zu verändern.
Für jede Achse (weiße Box) gibt es vier Pfeile, die direkt unterhalb der Box auf einem Schieber sitzen (die Schieberegler über der X-, Y- und Ruder-
Achse werden später erklärt) – zwei in der Mitte, und je einen weiteren an den beiden Enden. Die beiden mittleren beziehen sich auf den Mittelpunkt,
die beiden äußeren auf oberes bzw. unteres Ende der Achse.
Während Sie die linke Maustaste gedrückt halten, können Sie die Pfeile hin- und herschieben. Sie werden feststellen, dass sich immer zwei Pfeile
gleichzeitig bewegen. Das Bewegen von zwei Pfeilen zur gleichen Zeit hilft Ihnen, die Totzonen korrekt einzustellen. Sie können die Pfeile an jeden
beliebigen Punkt ziehen. Die grauen Bereichen, die beim Schieben der Pfeile erscheinen, zeigen die Bereiche der Totzonen an. Das nachfolgende Bild
zeigt das Beispiel eines Rotary, dessen Totzone am Mittelpunkt und an den beiden Enden vergrößert wurde.
Wenn nötig, können Sie die Pfeile auch unabhängig voneinander verschieben anstatt paarweise. Dies kann z.B. sinnvoll sein, wenn Sie am oberen
Ende der Achse eine Totzone benötigen, am unteren jedoch nicht. Rechtsklicken Sie hierzu irgendwo in die weiße Box und wählen Sie Link
Deadzones aus der Popup-Liste. Wenn Sie diesen Vorgang wiederholen, können Sie die Pfeile wieder paarweise verschieben.