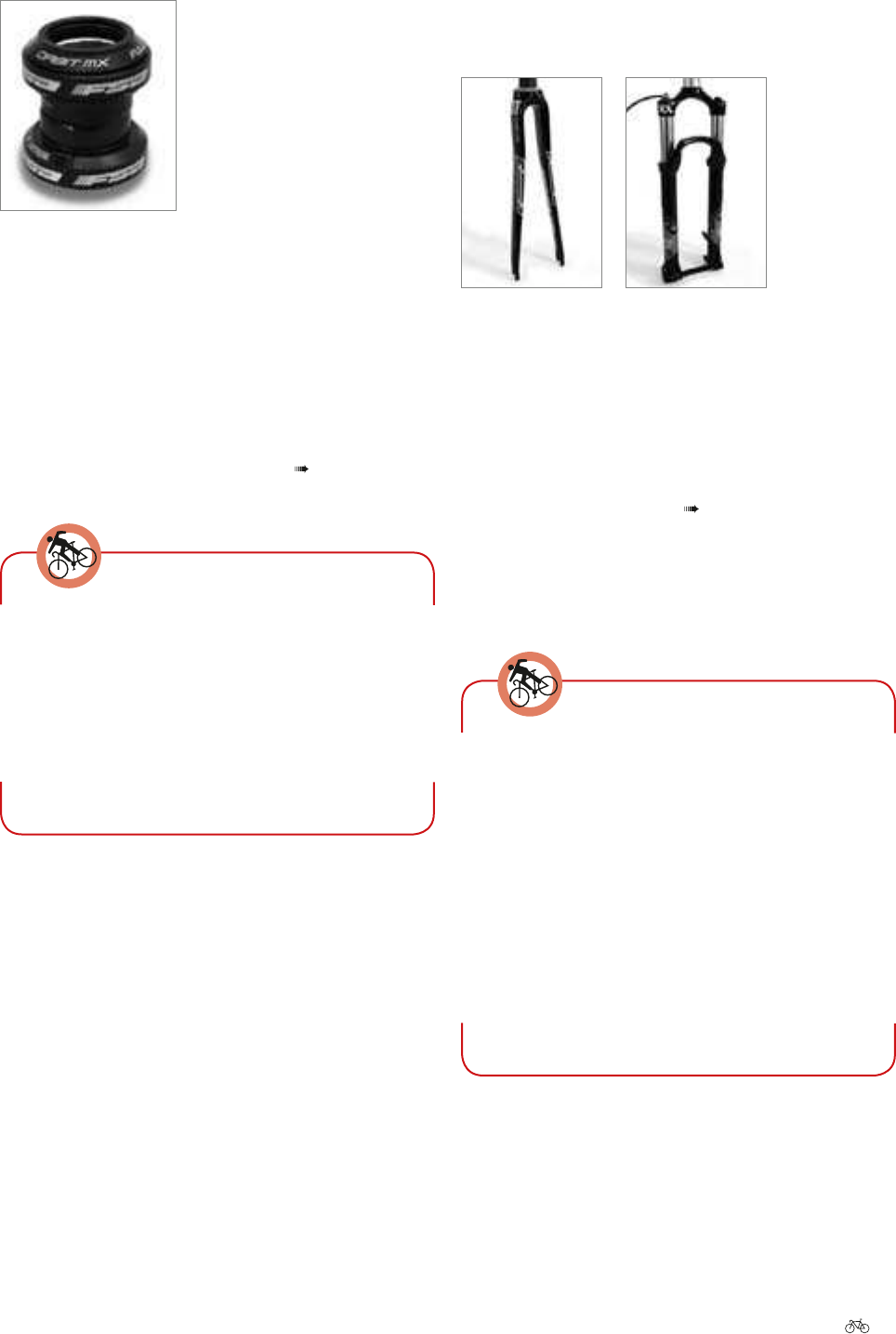
Headset
The headset is the bearing for the bike fork in the ame. If
the headset has been properly adjusted, it will turn easily.
In doing so, no play should be evident.
The headset is subject to a large amount of stress due to
impacts with the road surface. This can cause it to come
loose or aect its setting. Have the play and ease of move-
ment of the headset checked regularly by your specialist
cycle shop (for inspection intervals see
Chapter 28.1
"Inspection schedule").
Checking the headset
If you do not adjust the headset properly or tighten
it too tightly, this could cause breakages. This should
therefore always be carried out by a professional bike
workshop.
If you ride with the headset loose, this could damage
the bearing shells or fork.
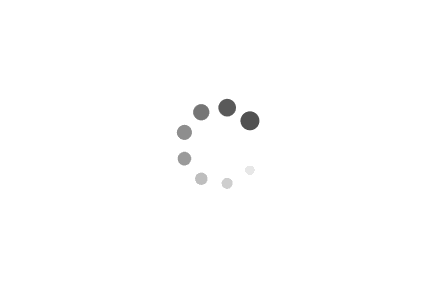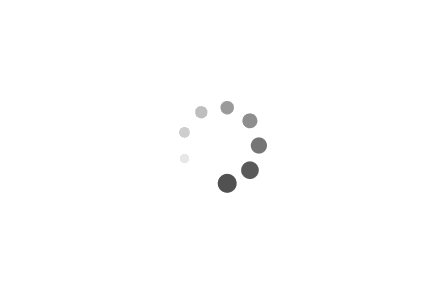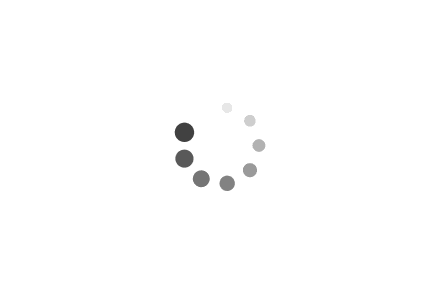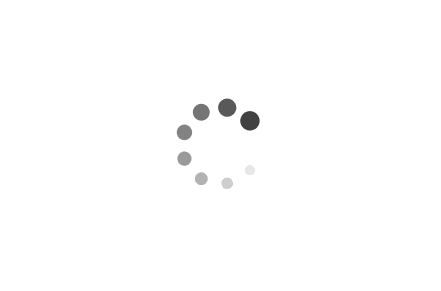
12 Fork
The ont wheel is held in place by the bike fork. The bike
fork consists of two fork blades, the fork crown and steer-
ing tube.
Carbon fork Suspension fork
The suspension fork is a feature of most mountain bikes,
trekking bikes and city bikes. They can be adjusted in
dierent ways and provide a greater degree of riding com-
fort.
For information on the nction, maintenance and care of
suspension elements, refer to
Chapter 13 "Suspension
ame and suspension elements". Specic information on
your suspension fork is provided in the manufacturer's
operating instructions which you can nd on the CD or the
manufacturer's website.
Never ride with a damaged bike fork. Do not attempt
to repair a defective bike fork. This can lead to serious
accidents. If you notice that the bike fork is warped or
otherwise damaged, replace it before using the bike
again.
Avoid sudden changes in ground level and riding o
high kerb stones. This can damage the fork and lead
to serious accidents.
Check regularly that the screws on the bike fork are
securely fastened. If screws are allowed to come
loose, this can cause serious accidents.