32 OPERATION
Operation
Digital Bitstream Indicators
When a digital source is playing, the AVR senses
the type of bitstream data that is present. Using
this information, the correct surround mode will
automatically be selected. For example, DTS bit-
streams will cause the unit to switch to DTS
decoding, and Dolby Digital bitstreams will enable
Dolby Digital decoding. When the unit senses
PCM data, from CDs and LDs and some music
DVDs or certain tracks on normal DVDs, it will
allow the appropriate surround mode to be select-
ed manually. Since the range of available surround
modes depends on the type of digital data that is
present, the AVR uses a variety of indicators to let
you know what type of signal is present. This will
help you to understand the choice of modes and
the input channels recorded on the disc.
When a digital source is playing, the AVR will
display a variety of messages to indicate the type
of bitstream received. These messages will appear
shortly after an input or surround mode is
changed, and will remain in the Main
Information Display
˜
for about five seconds
before the display returns to the normal surround
mode indication.
Surround Mode Types
For Dolby Digital and DTS sources, a three digit
indication will appear, showing the number of
channels present in the data. An example of this
type of display is 3/2/.1.
The first number indicates how many discrete
front channel signals are present.
• A 3 tells you that separate front left, center and
front right signals are available. This will be dis-
played for Dolby Digital 5.1 and DTS 5.1 pro-
grams.
• A 2 tells you that separate front left and right
signals are available, but there is no discrete
center channel signal. This will be displayed for
Dolby Digital bit streams that have stereo pro-
gram material.
• A 1 tells you that there is only a mono channel
available in the Dolby Digital bitstream.
The middle number indicates how many discrete
surround channel signals are present.
• A 2 tells you that separate surround left and
right signals are available. This will be displayed
for Dolby Digital 5.1 and DTS 5.1 programs.
• A 1 tells you that there is only a single, sur-
round encoded surround channel. This will
appear for Dolby Digital bit streams that have
matrix encoding.
• A 0 indicates that there is no surround channel
information. This will be displayed for two-
channel stereo programs.
The last number indicates if there is a discrete
Low Frequency Effects (LFE) channel. This is the
“.1” in the common abbreviation of “5.1” sound
and it is a special channel that contains only bass
frequencies.
• A .1 tells you that an LFE channel is present.
This will be displayed for Dolby Digital 5.1 and
DTS 5.1 programs, as available.
• A 0 indicates that there is no LFE channel infor-
mation available. However, even when there is
no dedicated LFE channel, low frequency sound
will be present at the subwoofer output when
the speaker configuration is set to show the
presence of subwoofer.
When Dolby Digital 3/2/.1 or DTS 3/2/.1 signals
are being played, the AVR will automatically
switch to the proper surround mode, and no
other processing may be selected. When a Dolby
Digital signal with a 3/1/0 or 2/0/0 signal is
detected you may select any of the Dolby sur-
round modes.
It is always a good idea to check the readout for
the channel data to make certain that it matches
the audio logo information shown on the back of
a DVD package. In some cases you will see indi-
cation for “2/0/0” even when the disc contains a
full 5.1, or 3/2/.1 signal. When this happens,
check the audio output settings for your DVD
player or the audio menu selections for the spe-
cific disc being played to make certain that the
player is sending the correct signal to the AVR.
PCM Playback Indications
PCM is the abbreviation for Pulse Code
Modulation, which is the type of digital signal
used for standard CD playback, and other non-
Dolby Digital and non-DTS digital sources such as
Mini-Disc. When a PCM signal is detected, the
Main Information Display
˜
will briefly
show a message with the letters PCM, in addition
to a readout of the sampling frequency of the
digital signal.
In most cases this will be
48 KHZ, though in
the case of specially mastered, high-resolution
audio discs you will see a
96 KHZ indication.
The
PCM 48 KHZ indication will also appear
when modes or inputs are changed for analog
sources. In those cases the system is telling you
the sampling frequency used internally at the
output of the analog-to-digital converters that
change the incoming signal from a VCR, tape
deck, the tuner, or other ana-log source to digital.
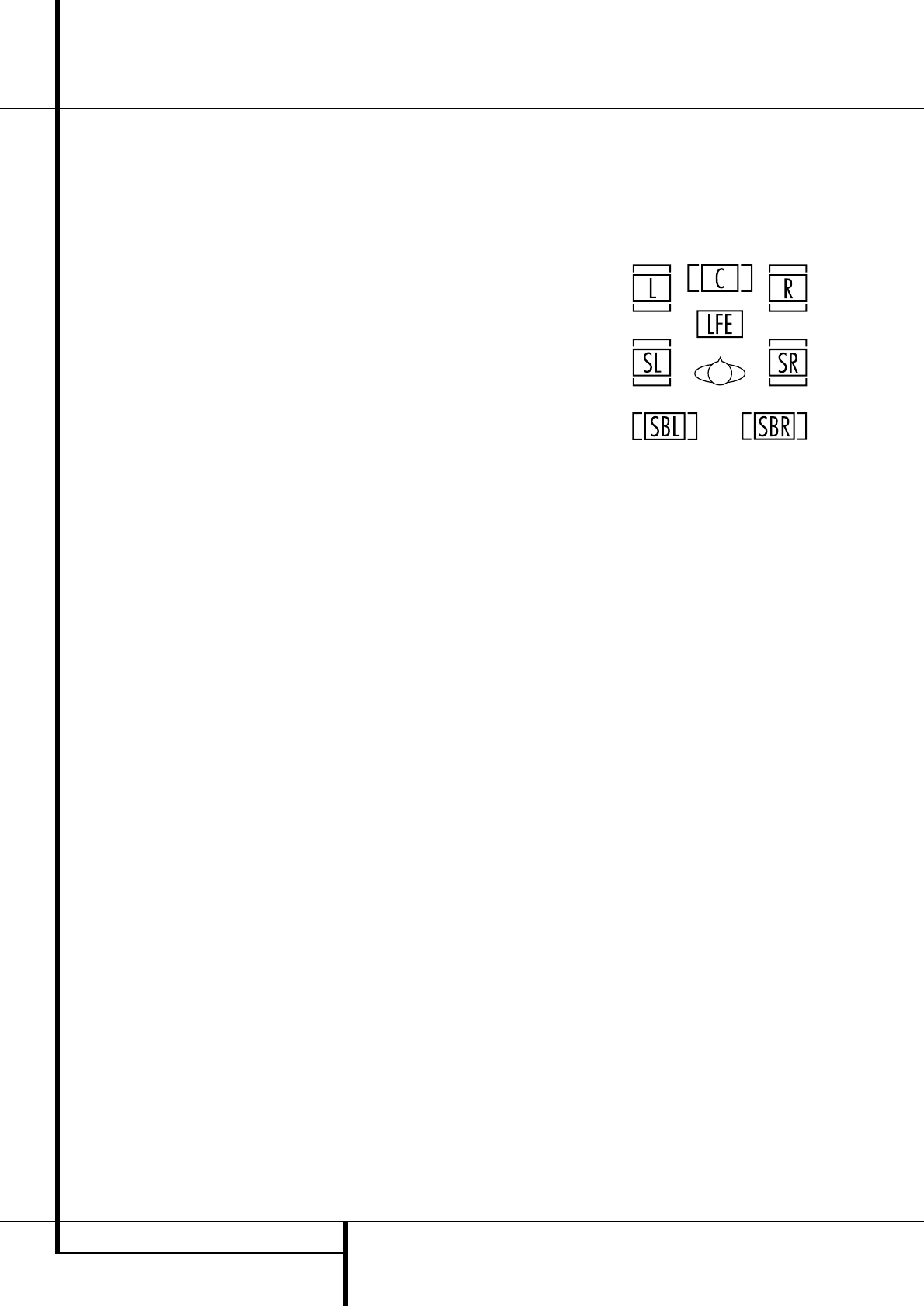
Speaker/Channel Indicators
In addition to the Bitstream Indicators, the
AVR features a set of unique channel-input
indicators that tell you how many channels of
digital information are being received and/or
whether the digital signal is interrupted.
(See Figure 9).
Figure 9
These indicators are the L/C/R/LFE/SL/SR/SBL/SBR
letters that are inside the center boxes of the
Speaker/Channel Input Indicators
$
in the
front panel Main Information Display
˜
.
When a standard analog stereo or matrix
surround signal is in use, only the “L” and “R”
indicators will light, as analog signals have only
left and right channels.
Digital signals, however, may have one, two, five,
six or seven separate channels, depending on the
program material, the method of transmission
and the way in which it was encoded. When a
digital signal is playing, the letters in these
indicators will light in response to the specific
signal being received. It is important to note that
although Dolby Digital, for example, is referred to
as a “5.1” system, not all Dolby Digital DVDs or
audio tracks selected on DVD or other Dolby
Digital programs are encoded for 5.1. Thus, it is
sometimes normal for a DVD with a Dolby Digital
soundtrack to trigger only the “L” and “R”
indicators.
NOTE: Many DVD discs are recorded with both
“5.1” and “2.0” versions of the same sound-
track. When playing a DVD, always be certain to
check the type of material on the disc. Most discs
show this information in the form of a listing or
icon on the back of the disc jacket. When a disc
does offer multiple soundtrack choices, you may
have to make some adjustments to your DVD
player (usually with the “Audio Select” button or
in a menu screen on the disc) to send a full 5.1
feed to the AVR or to select the appropriate
audio track and thus language. It is also possible
for the type of signal feed to change during the
course of a DVD playback. In some cases the pre-
views of special material will only be recorded in
2.0 audio, while the main feature is available in
5.1 audio. As long as your DVD player is set for
6-channel output, the AVR will automatically