12
Microwave oven is a Group 2 ISM equipment in which radio frequency energy is intentionally generated and used in the form of
electromagnetic radiation for the treatment of material. This oven is a Class B equipment suitable for use in domestic
establishments and in establishments directly connected to a low voltage power supply network which supplies buildings used for
domestic purposes.
WEIGHT MMEASURES
15 g
1
/
2
oz.
25 g 1 oz.
50 g 2 oz.
100 g 4 oz.
175 g 6 oz.
225 g 8 oz.
450 g 1 lb.
VOLUME MMEASURES
30 ml 1 fl.oz.
100 ml 3 fl.oz.
150 ml 5 fl.oz. (
1
/
4
pt)
300 ml 10 fl.oz. (
1
/
2
pt)
600 ml 20 fl.oz. (1pt)
SPOON MMEASURES
1.25 ml
1
/
4
tsp
2.5 ml
1
/
2
tsp
5 ml 1 tsp
15 ml 1 tbsp
FLUID MMEASUREMENTS
1 Cup = 8 fl.oz.= 240 ml
1 Pint = 16 fl.oz. (UK 20 fl.oz.) = 480 ml (UK 560 ml)
1 Quart = 32 fl.oz. (UK 40 fl.oz.) = 960 ml (UK 1120 ml)
1 Gallon = 128 fl.oz. (UK 160 fl.oz.) = 3840 ml (UK 4500 ml)
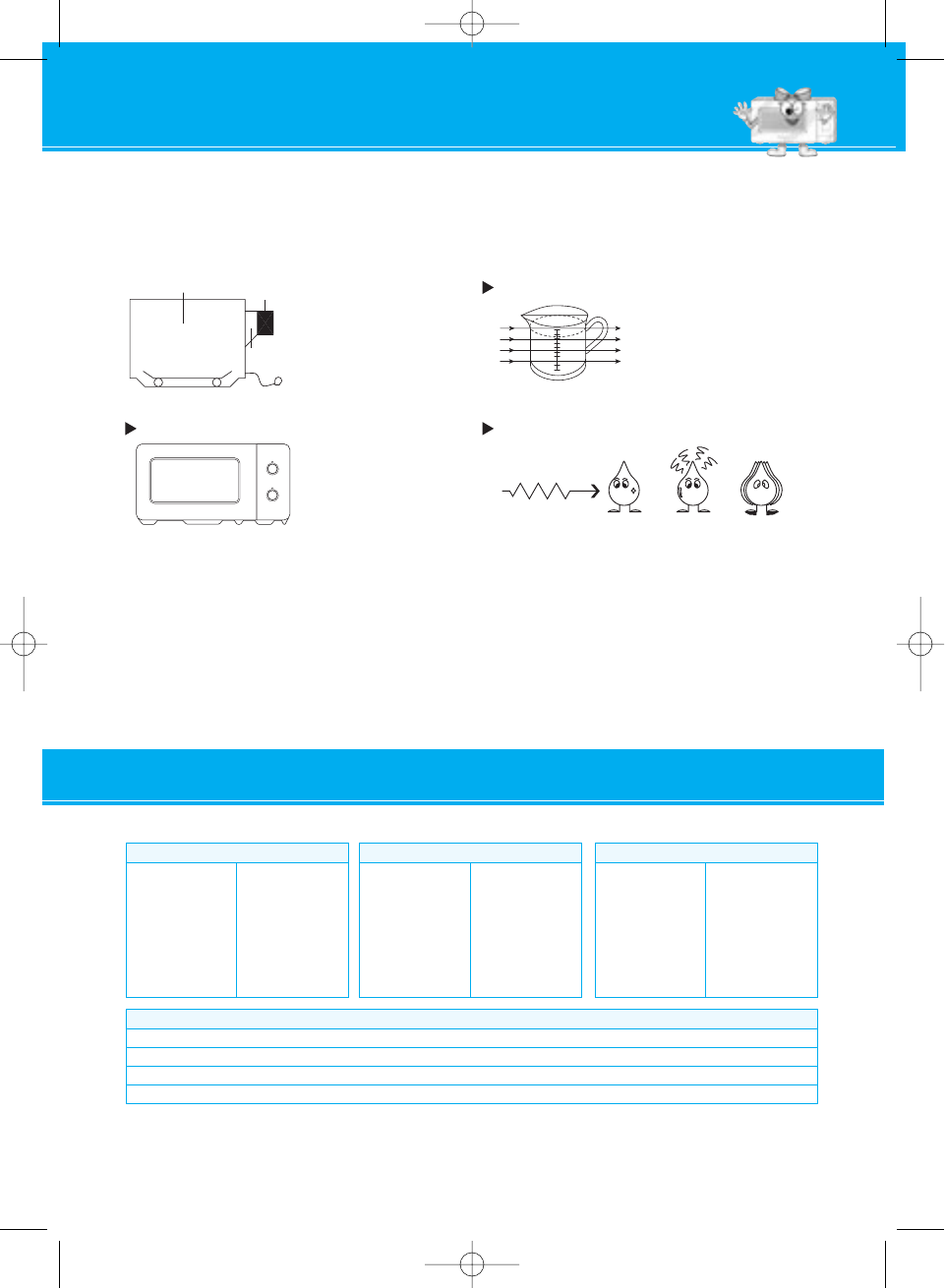
Then they pass through the
cooking containers to be
absorbed by the water
molecules in the food, all foods
contain water to a more or
lesser extent.
The microwaves cause the water molecules to vibrate which
causes FRICTION, i.e. HEAT. This heat then cooks the food.
Microwaves are also attracted to fat and sugar particles, and
foods high in these will cook more quickly. Microwaves can
only penetrate to a depth of
4-5cm and as heat spreads through the food by conduction,
just as in a traditional oven, the food cooks from the outside
inwards.
In a microwave oven,
electricity is converted into
microwaves by the
MAGNETRON.
The microwaves bounce
off the metal walls and the
metal door screen.
Oven Cavity
Magnetron
Waveguide
Turntable
REFLECTION
TRANSMISSION
ABSORPTION
Microwave Water Molecule Absorption Vibration
HOW MICROWAVES COOK FOOD
CONVERSION CHARTS